Bypassing NAT: Difference between revisions
(→Ngrok) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
IPv4 address space is limited and therefore to connect many devices to the Internet a special | |||
mechanisms are being used. Internet service providers usually share same IP address between | |||
several people. WiFi routers are also share single external IP address between multiple connected | |||
devices. This is implemented through NAT, depending on your network setup it can be local or carrier-grade. | |||
Your device is not accessible from the Internet by default, if behind NAT. If you are under | |||
carrier-grade NAT or can't modify router settings (port forwarding), read below for the | |||
solutions how to make your device accessible from the Internet. | |||
You do not need this if you have subscribed to mobile carrier's static IP service or were able | |||
to setup port forwarding in your WiFi router settings. | |||
== Tor == | == Tor == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 24: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
You may want to install a ` | You may want to install a `proxychains-ng` for accessing the Tor Network: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
pkg install | pkg install proxychains-ng | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Package `torsocks` may not work since Android 8. | |||
=== Setting up Onion Service === | === Setting up Onion Service === | ||
You will have to modify the default configuration file of tor (<code>$PREFIX/etc/tor/torrc</code>). Here is an example of configuring SSH Onion Service: | You will have to modify the default configuration file of tor (<code>$PREFIX/etc/tor/torrc</code>). Here is an example of configuring SSH Onion Service, overwrite the torrc file with this content: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
## Enable TOR SOCKS proxy | ## Enable TOR SOCKS proxy | ||
| Line 44: | Line 55: | ||
=== Accessing your service === | === Accessing your service === | ||
First of all make sure that on client device `tor` is running and you have all necessary software for accessing Tor Network (in this case package ` | First of all make sure that on client device `tor` is running and you have all necessary software for accessing Tor Network (in this case package `proxychains-ng`). | ||
To access the onion service created in previous step, run this: | To access the onion service created in previous step, run this: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
proxychains4 ssh g3yv3tvqrbow7koz.onion | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 70: | Line 81: | ||
'''Terms of service''': https://ngrok.com/tos | '''Terms of service''': https://ngrok.com/tos | ||
''' | '''Pricing''': https://ngrok.com/pricing | ||
'''Free tier''': 40 connections per minute, 4 tunnels max. | |||
'''Termux developers are not responsible about availability, reliability and safety of this service !''' | '''Termux developers are not responsible about availability, reliability and safety of this service !''' | ||
=== | === Using Ngrok === | ||
You may want to use Ngrok without installing its client which is closed-source and is not working | |||
in Termux out-of-box. See instructions below for doing setup to be able make tunnels with OpenSSH. | |||
[[File:Ngrok-add-ssh-pubkey.png|thumb|Adding a new OpenSSH key to Ngrok account.]] | |||
Here will be assumed that you already have Ngrok account on at least Free plan. | |||
1. | 1. Install OpenSSH. | ||
pkg install openssh | |||
2. | 2. Generate a pair of private and public keys. Skip if you already have the key. | ||
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa | |||
3. | 3. Go to https://dashboard.ngrok.com/auth/ssh-keys/new and paste public key into text field. Then click "Add". Your SSH key should be assigned to your account. | ||
4. Now start a server and run next command to do a port forwarding. | |||
ssh -R 0:localhost:${PORT} tunnel.us.ngrok.com tcp ${PORT} | |||
Where ${PORT} is a local port which you want to expose. See an example of OpenSSH port forwarding: | |||
<pre> | |||
~ $ ssh -R 0:localhost:8022 tunnel.us.ngrok.com tcp 8022 | |||
Allocated port 10585 for remote forward to localhost:8022 | |||
ngrok (via SSH) by @inconshreveable (Ctrl+C to quit) | |||
Account <CENSORED> (Plan: Free) | |||
Region us | |||
Forwarding tcp://2.tcp.ngrok.io:10585 | |||
< | |||
Region | |||
Forwarding | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Please note that Ngrok TCP forwarding will assign a random port for free accounts. | |||
More examples on this topic at https://ngrok.com/docs#ssh-gateway-examples. | |||
== Tmate == | == Tmate == | ||
Latest revision as of 13:43, 4 November 2021
IPv4 address space is limited and therefore to connect many devices to the Internet a special mechanisms are being used. Internet service providers usually share same IP address between several people. WiFi routers are also share single external IP address between multiple connected devices. This is implemented through NAT, depending on your network setup it can be local or carrier-grade.
Your device is not accessible from the Internet by default, if behind NAT. If you are under carrier-grade NAT or can't modify router settings (port forwarding), read below for the solutions how to make your device accessible from the Internet.
You do not need this if you have subscribed to mobile carrier's static IP service or were able to setup port forwarding in your WiFi router settings.
Tor
Accessing device via Tor is the most secure and effective method - offers strong end-to-end encryption (onion services don't use 'exit' node), virtual ports (e.g. 80 port without root), your service won't be visible on plain Internet.
However, this method requires setting up a Tor Onion Service.
Installing needed packages
The main package is tor. Install it by running this command:
pkg install tor
You may want to install a `proxychains-ng` for accessing the Tor Network:
pkg install proxychains-ng
Package `torsocks` may not work since Android 8.
Setting up Onion Service
You will have to modify the default configuration file of tor ($PREFIX/etc/tor/torrc). Here is an example of configuring SSH Onion Service, overwrite the torrc file with this content:
## Enable TOR SOCKS proxy SOCKSPort 127.0.0.1:9050 ## Hidden Service: SSH HiddenServiceDir /data/data/com.termux/files/home/.tor/hidden_ssh HiddenServicePort 22 127.0.0.1:8022
Then you need to make a directory where information about Hidden Service will be stored:
mkdir -p ~/.tor/hidden_ssh
Now you can execute in console tor. If start was successfull, you can get your onion service hostname:
cat ~/.tor/hidden_ssh/hostname
Output should be like this: g3yv3tvqrbow7koz.onion
Accessing your service
First of all make sure that on client device `tor` is running and you have all necessary software for accessing Tor Network (in this case package `proxychains-ng`).
To access the onion service created in previous step, run this:
proxychains4 ssh g3yv3tvqrbow7koz.onion
If everything is ok, the output should be like this:
The authenticity of host 'g3yv3tvqrbow7koz.onion (127.42.42.0)' can't be established. ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:WGualHEq7SJdvVeXgy8a+btPQCd7uxTeXjlWdHHLwLc. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
Remember, `tor` should be running on both (client/server) sides, otherwise you will get connection errors. You can configure other servers (e.g. Nginx) in the same way as shown in above example for SSH.
Learn more about Onion Services
Better explanation about Onion Services and other Tor-related things you can found at torproject.org.
Ngrok
Homepage: https://ngrok.com/
Terms of service: https://ngrok.com/tos
Pricing: https://ngrok.com/pricing
Free tier: 40 connections per minute, 4 tunnels max.
Termux developers are not responsible about availability, reliability and safety of this service !
Using Ngrok
You may want to use Ngrok without installing its client which is closed-source and is not working in Termux out-of-box. See instructions below for doing setup to be able make tunnels with OpenSSH.
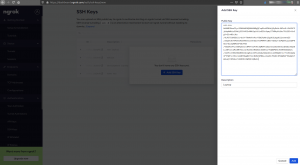
Here will be assumed that you already have Ngrok account on at least Free plan.
1. Install OpenSSH.
pkg install openssh
2. Generate a pair of private and public keys. Skip if you already have the key.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
3. Go to https://dashboard.ngrok.com/auth/ssh-keys/new and paste public key into text field. Then click "Add". Your SSH key should be assigned to your account.
4. Now start a server and run next command to do a port forwarding.
ssh -R 0:localhost:${PORT} tunnel.us.ngrok.com tcp ${PORT}
Where ${PORT} is a local port which you want to expose. See an example of OpenSSH port forwarding:
~ $ ssh -R 0:localhost:8022 tunnel.us.ngrok.com tcp 8022 Allocated port 10585 for remote forward to localhost:8022 ngrok (via SSH) by @inconshreveable (Ctrl+C to quit) Account <CENSORED> (Plan: Free) Region us Forwarding tcp://2.tcp.ngrok.io:10585
Please note that Ngrok TCP forwarding will assign a random port for free accounts.
More examples on this topic at https://ngrok.com/docs#ssh-gateway-examples.
Tmate
Tmate is utility for sharing terminals. It is very easy to use, though it will destroy connection once client disconnected.
Utility can be installed with pkg install tmate.
Usage example
1. Make sure that all your devices have SSH key in ~/.ssh directory. If not, on each device do:
pkg install openssh mkdir ~/.ssh ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
2. Execute the following command within Termux:
tmate
3. Once you done previous step, you should see a colored line at the screen bottom with link. Save it, because it is your connection token. It looks like
Bff5fhJquRpO105c3OL62Icfp@fk2.tmate.io
4. On another device from which you want to connect to Termux, run
ssh Bff5fhJquRpO105c3OL62Icfp@fk2.tmate.io
Important note: link shown above is just example and should not be copy-pasted !